Since you opened this page, 0 cows, bulls and buffaloes were killed in India

A Typical Dairy Cow/Buffalo Goes through Following Steps
Step 1: Forced Impregnation
A Cow/buffalo starts producing milk only when she gives birth. Thus, the first step in a dairy farm is to get her impregnated.
a) Artificial insemination
-
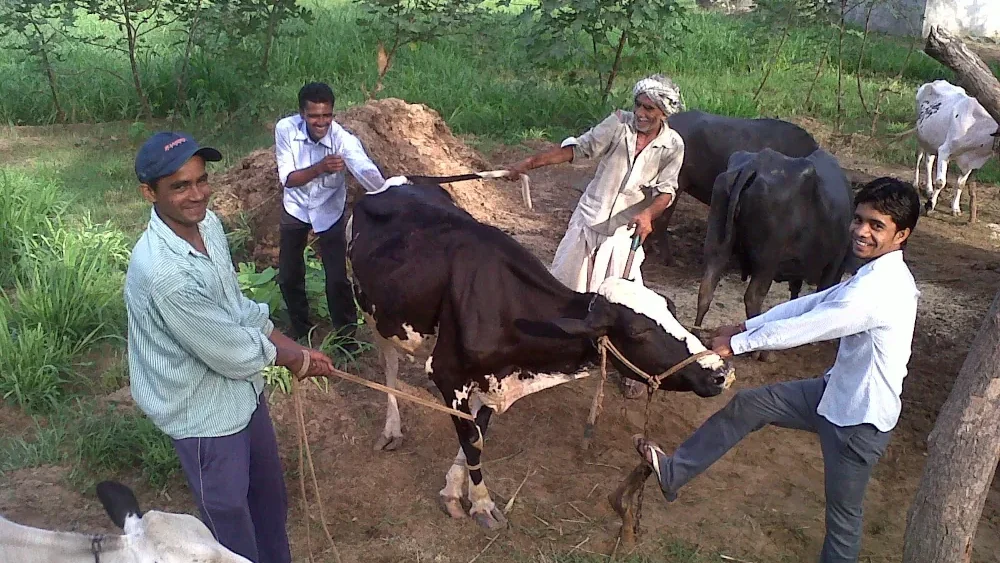
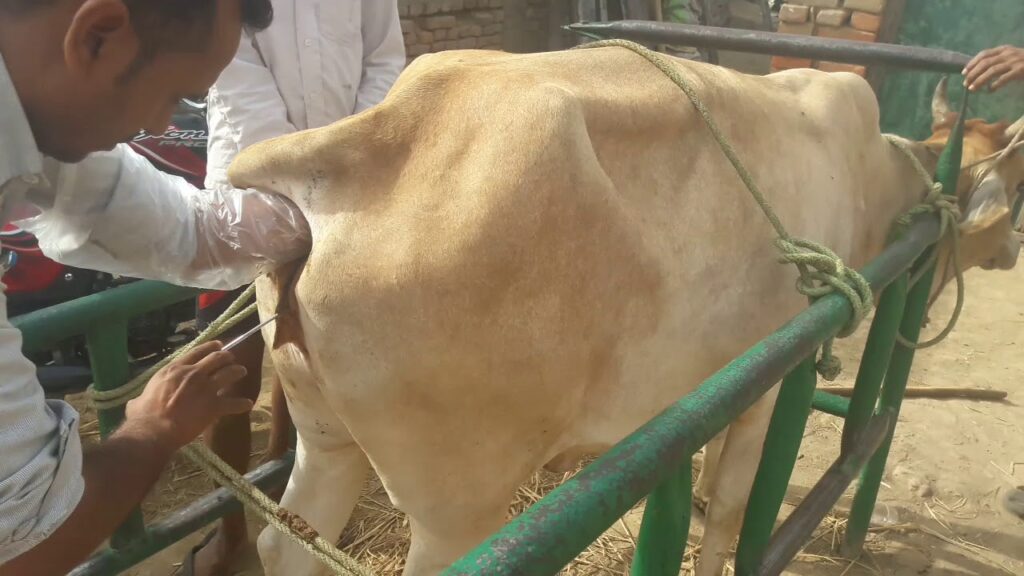


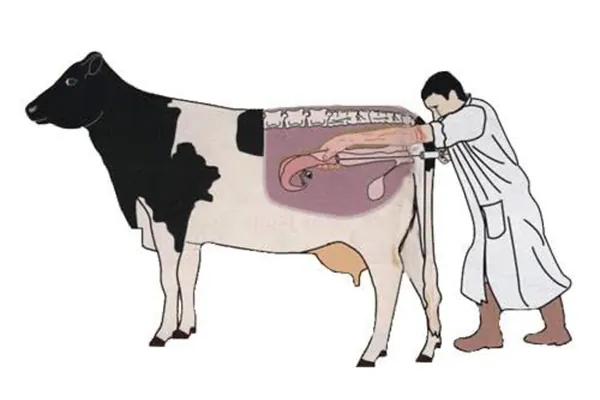
In many states, Artificial insemination is the most common way of impregnating a cow/buffalo. Cows and buffaloes are either tied or forced inside a rack (called a rape rack) so that they cannot resist. The most common type of artificial insemination is called Recto Vaginal Method. Here, the inseminator will insert the gloved left hand into the rectum, and the hand is further inserted and will catch hold of the cervix through the rectal wall. The insemination gun loaded with semen straw is passed through the vulva to the vagina and cervix and observed with the hand in the rectum that the insemination gun reaches the cervix, then the semen is deposited by injecting the gun!
Other methods of artificial insemination include placing a spectrum in the vagina of the cow, then passing the inseminating tube through it, or a direct method where the entire hand holding the inseminating tube is passed through the vagina! Click for source
This is not a necessary medical procedure to save/improve her life. This is done solely for human gain. As you can imagine, the process is painful and unnatural. The term “artificial insemination” sugarcoats what this process is – RAPE! This is done to her starting from a very young age!
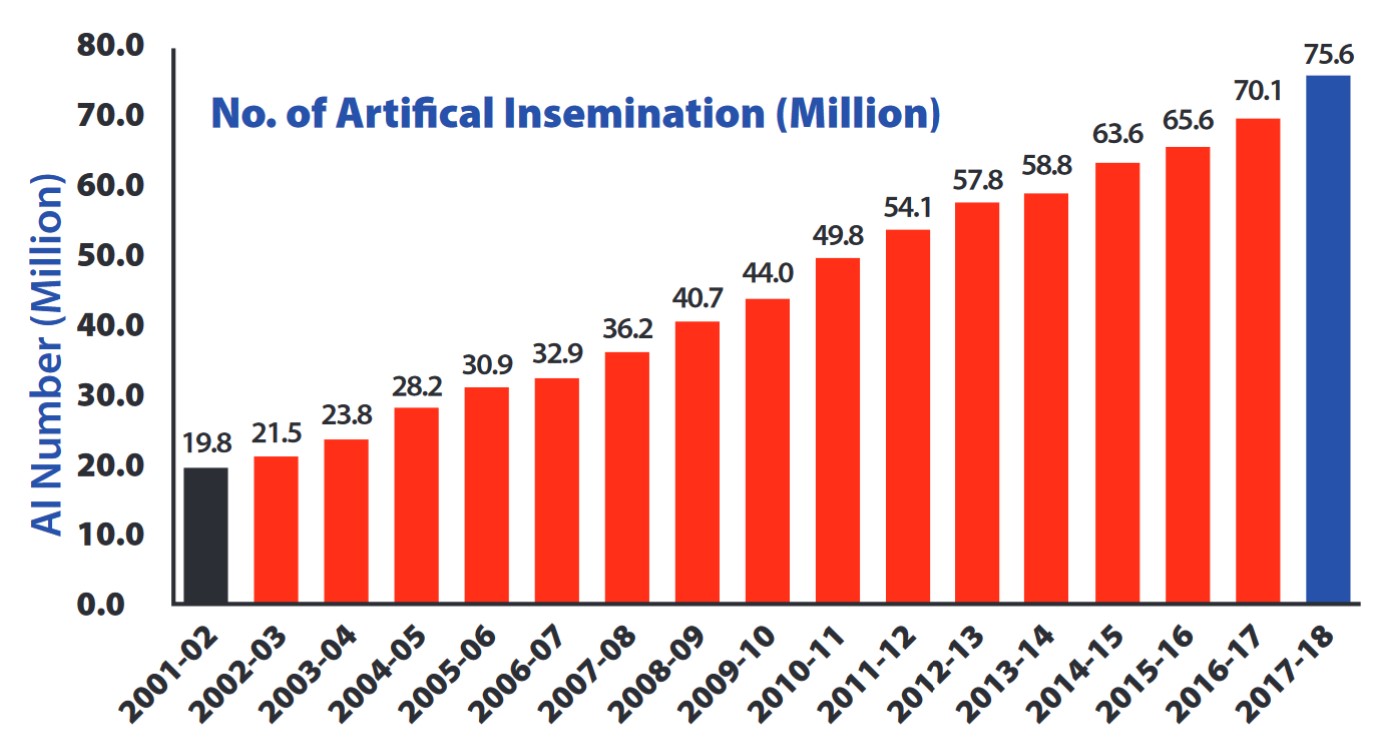
The rates of artificial insemination vary widely across states. For instance in Kerala, 99% of all inseminations were done artificially, while in Sikkim, Assam, Manipur, etc, the coverage is less than 5% (as of 2018). Since Artificial insemination reduces the cost of feeding and transporting males, the Indian government has heavily invested resources in promoting artificial insemination. The government’s “Rashtriya Gokul Mission” and Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme (NAIP) are sending artificial insemination training personnel and equipment to every village. They aim to have more than 90% of inseminations in all the states done in this way!
As a result, the use of artificial insemination is growing rapidly each year, and both small-scale farmers and large dairy farms are adopting it.
Also read: India imports bull semen from Brazil to raise milk production
b) So-Called “Natural” Method of Impregnation
-
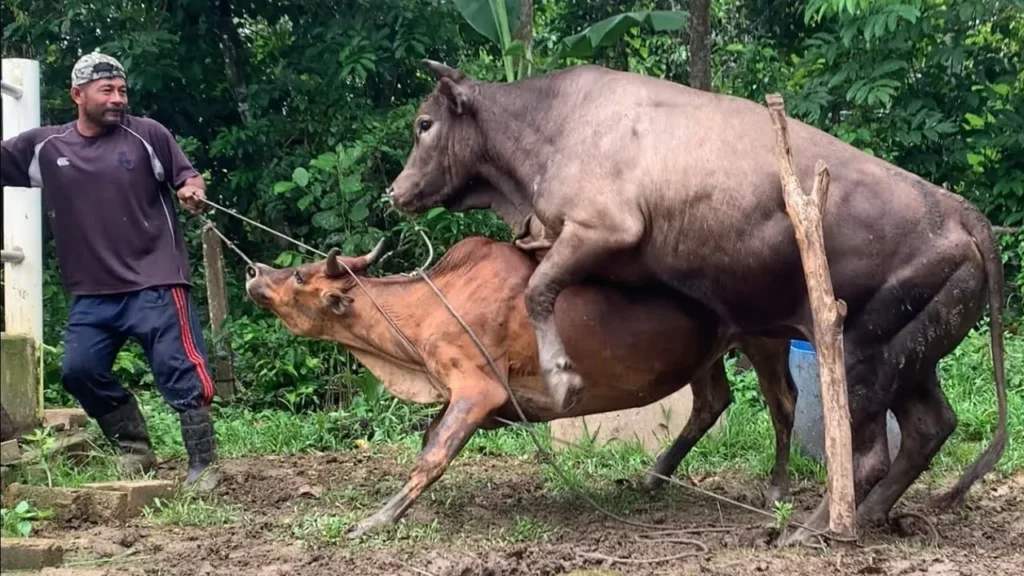

In this “natural mating” method, the female cow or buffalo is often restrained. The female does not choose the bull. He is selected and brought by the farmer, and she is tied up while the male mounts her. Thus this, too, constitutes a form of sexual assault on the animal.
Hence this too qualifies as “forced impregnation“. Starting as early as 1.5 years to 3 years old, cows and buffaloes undergo such forced insemination annually. It often takes several attempts to achieve a single pregnancy, and these animals are typically made to go through about 5 to 6 pregnancies during their shortened lifespan.
Read: Natural insemination is rapidly becoming a thing of the past
Step 2: Limiting/Starving the calf from drinking the milk
When a calf is born, the mother produces milk solely for the baby. Unfortunately, the aim of a dairy farm is to earn profit by selling the milk.
a) Limiting the Calf
There are no animals in nature that produce extra milk. Humans have genetically modified and selectively bred them to essentially become factories of milk. We have done this purely out of greed. Such unnatural animals have a difficult life as their body has to spend immense energy and resources to produce huge quantities of milk.
The ethical solution for this is simply not to breed animals into such unnatural bodies.
Most people are conditioned to view farm animals as mere commodities. This is why even though some breeds produce more milk, the calf is still not allowed to drink what it requires. Calves require milk equal to 15% to 20% of their body weight twice a day. However, they are denied that as well and are switched to solid food as soon as possible.
Why is this done? It’s because every drop that the calf drinks is a drop that cannot be sold. To ensure profit, farmers have to limit the calf from drinking the milk.
When a cow/buffalo is normally milked, there is still some residual milk left in her body. Many people extract this as well. To do so, an illegal, but widely used hormone called oxytocin is injected which causes incredible pain and forces the animal to release the extra milk!
b) Starving the Male Calf and Making Him “Khal Baccha”


Males are of no use to the dairy industry. They do not produce milk and because of artificial insemination, only one male is needed for impregnating thousands of females. Besides, the ease of use of tractors has significantly reduced the use of males for farming. Hence, keeping the male calf alive is nothing but a burden for the business.
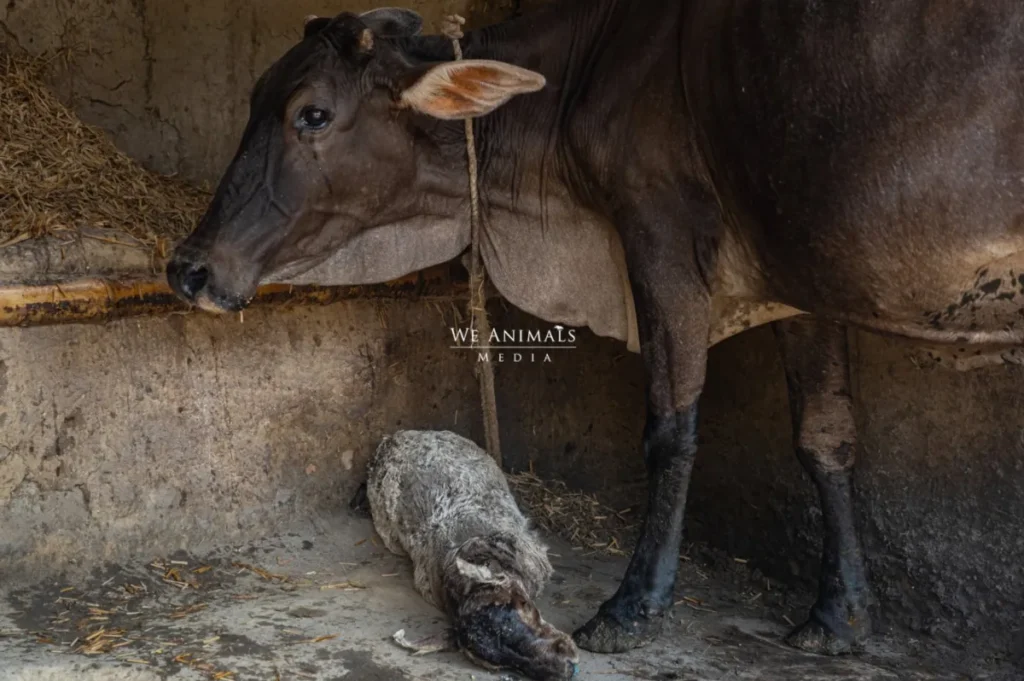
If the calf is no longer within the mother’s sight, the mother may stop lactating. That’s because the mother produces the milk only for her baby, not for us. So one way to get rid of this “burden” and still get milk from the mother is by making him a “khal baccha”.
Here, the baby is tied up in front of the mother so that she keeps on lactating. All the milk produced is taken by the farmer. When the calf dies of starvation (or diseases due to extreme unhygienic conditions), his body is filled with hay. This is now called khal baccha. This dead body is kept in front of the mother. The mother thinks her baby is still alive and keeps on producing milk. This milk is again taken and sold by humans for profit.
Step 3: Slaughter of Calves for Beef
India is the second largest exporter of beef in the world!
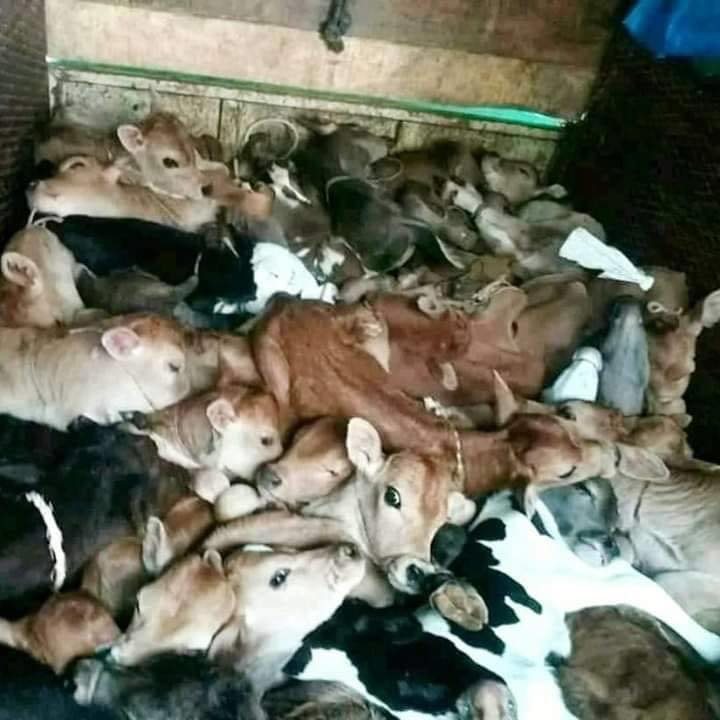
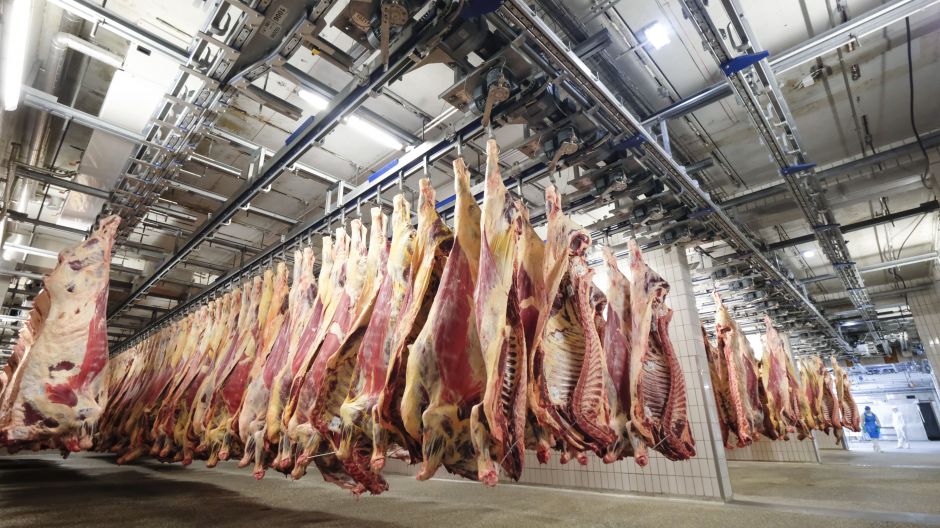


As mentioned earlier, males are of no use to the dairy industry. The best way to get rid of males is to sell them to slaughter! Even females in a lot of cases face the same fate. Once the mother dries up, the calves that were denied the required amount of milk and instead fed substitute solid foods are then loaded up in trucks to be slaughtered for beef and leather.
Laws regarding the slaughter of calves are different in different states. So to bypass them, they are legally or illegally transported to states where the slaughter is legal.
As a result, only 8.5% of total buffaloes in India are male! 91.5% are female. In cattle, males are 25% and females 75% – still nowhere near the natural ratio of around 50-50.
Source: Livestock Census 2019
Step 4: Repeat Steps 1, 2, and 3
At around 2 years of age, the cow/buffalo is forcefully impregnated for the first time. All the above steps are repeated every year for about 4-5 years.
Step 5: Slaughter of the Mother
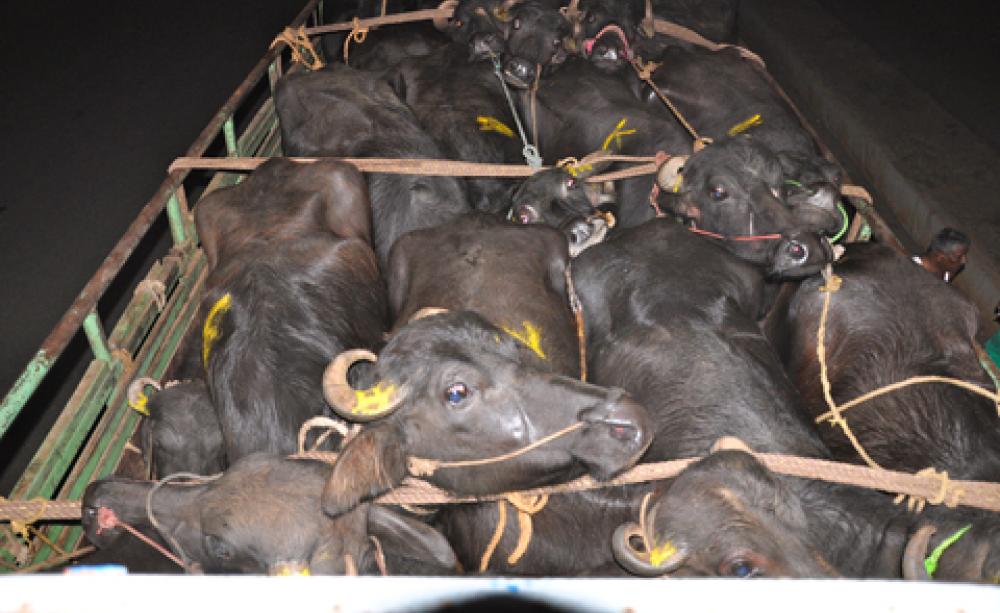
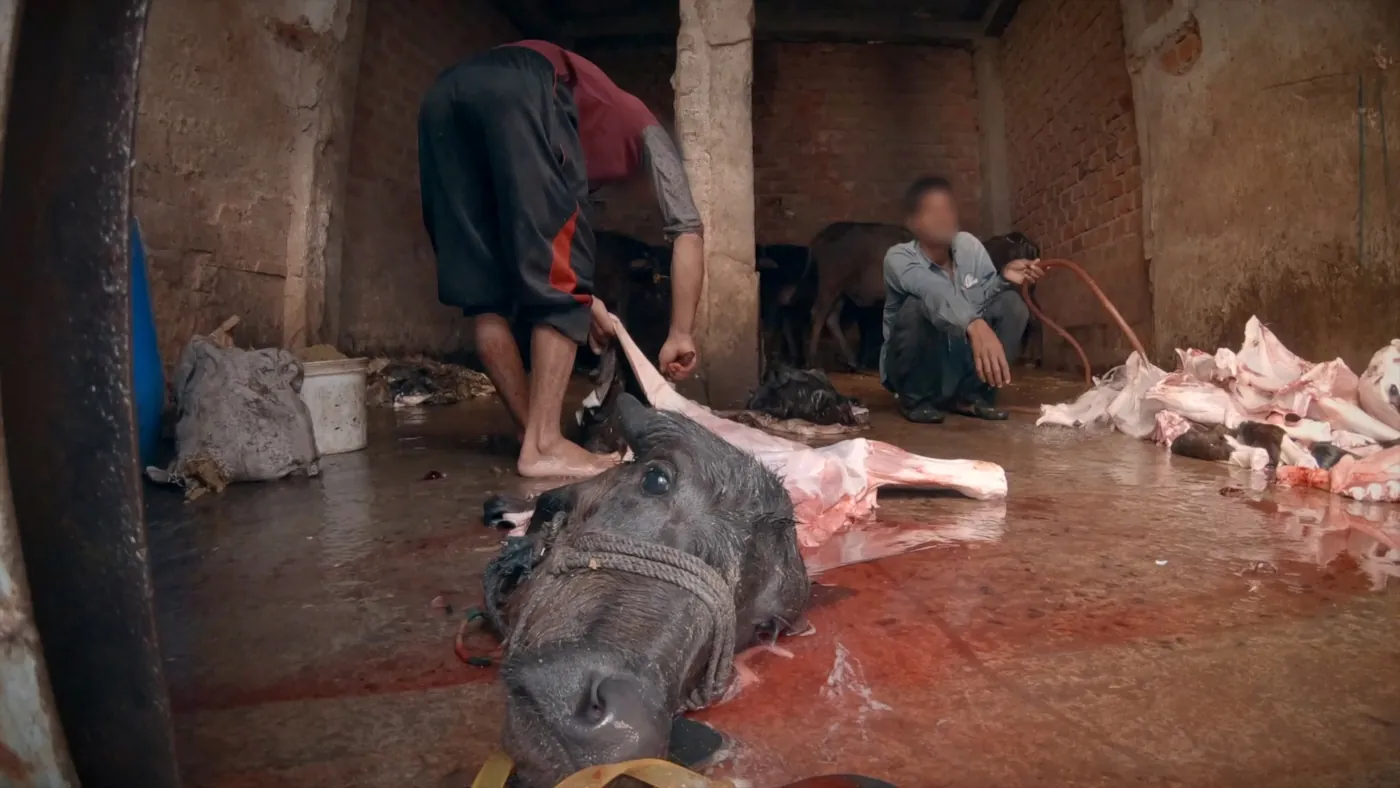

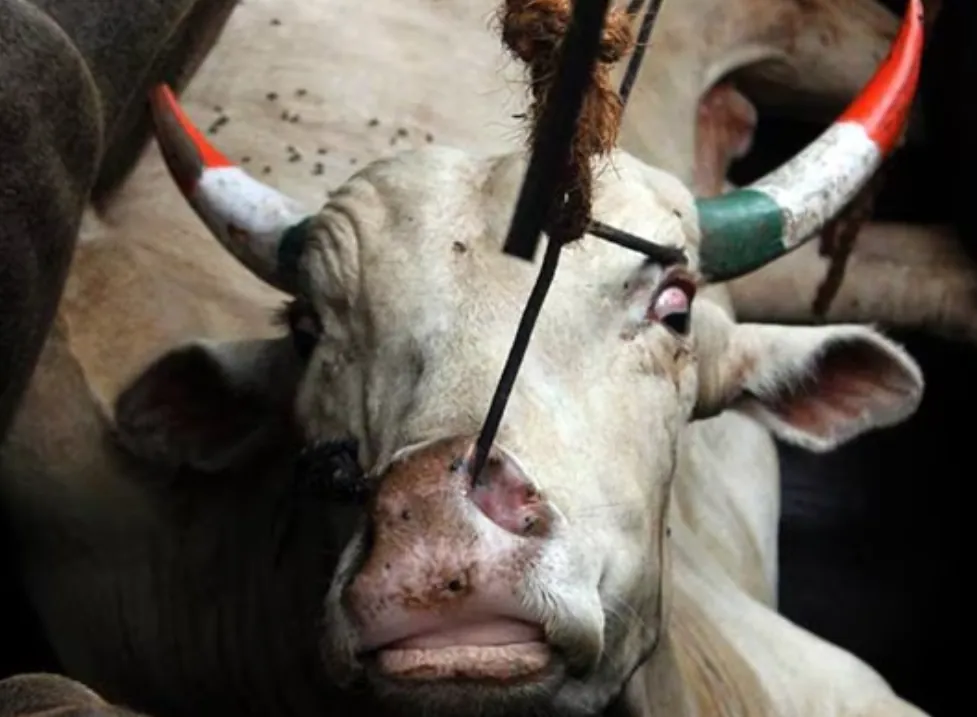

After living a horrible life, full of physical and mental torture, the cow/buffalo is finally sold for slaughter at 1/3rd of her natural lifespan. After 4-5 back-to-back pregnancies, and injections of oxytocin, her body starts breaking and her yield of milk lowers. In such a case, it is profitable for the farmer to get rid of the mother and force impregnate one of her daughters instead.
Money from selling the animals for slaughter is what enables the farmers to sell the milk at ₹30-35 per liter to companies like Amul. The beef industry, leather industry, and the dairy industry are one and the same. This is the reason why India is the largest producer of milk and the second-largest exporter of beef in the world!
On average, 20% of cows/buffaloes sent to slaughter are pregnant!
Other Cruelty in Dairy
The list of cruelty in dairy goes on and on.
Oxytocin
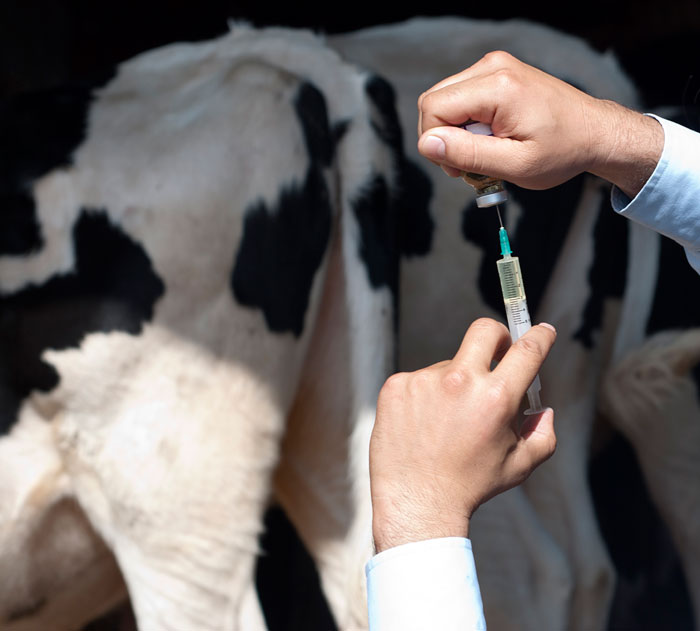

Oxytocin is an illegal drug that is injected in lactating cows/buffaloes. It is used to extract extra/residual milk that cannot be extracted with normal milking.
The drug is illegal because it enters the milk and when consumed by humans, it causes many health complications. When consumed, such milk causes early puberty in girls, breast enlargement in boys, and reduced testosterone in men. In pregnant women, it can cause abortion, deformities, or weak immunity in newborns. The use of such milk also increases the risk of hemorrhage in mothers after birth.
Source: Science for Agriculture and Allied Sector
Although illegal, the use of oxytocin is rampant in India and is cheap and easily available. When injected into cattle, it causes them to suffer severe stomach cramps as though they were in labor!
Watch: Widespread use of Oxytocin
Hygiene
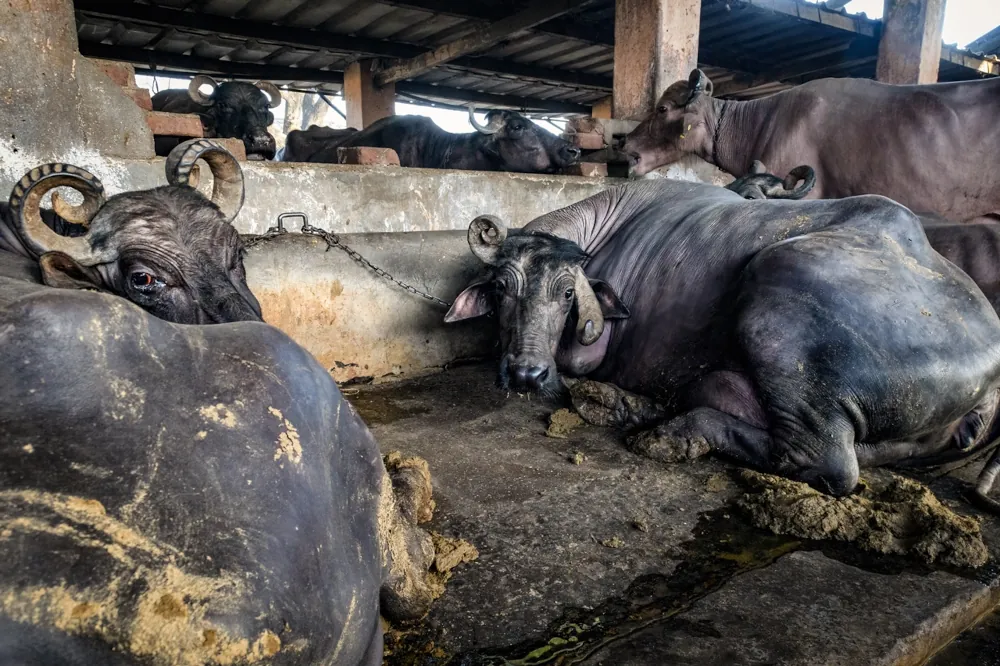
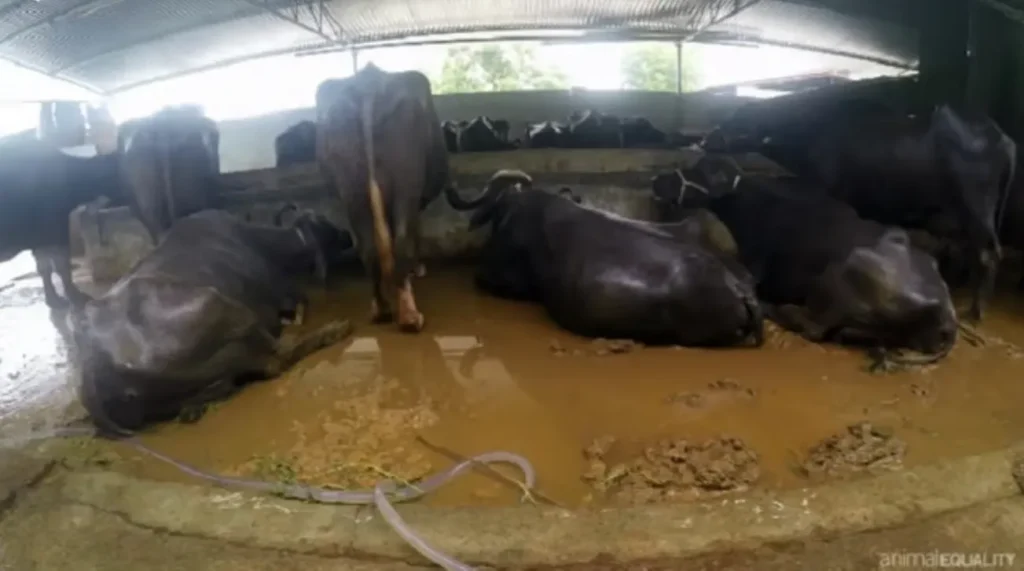


Visit any dairy farm in India and you’ll see cows and buffaloes lying in their feces and urine. Although many Indians consider cow dung and urine as holy, for the animals it is still feces and urine.
Such unhygienic conditions coupled with the fact that animals are close to each other makes the farm a hotbed for diseases. To counter these diseases, the animals are given extreme amounts of antibiotics!
Mastitis
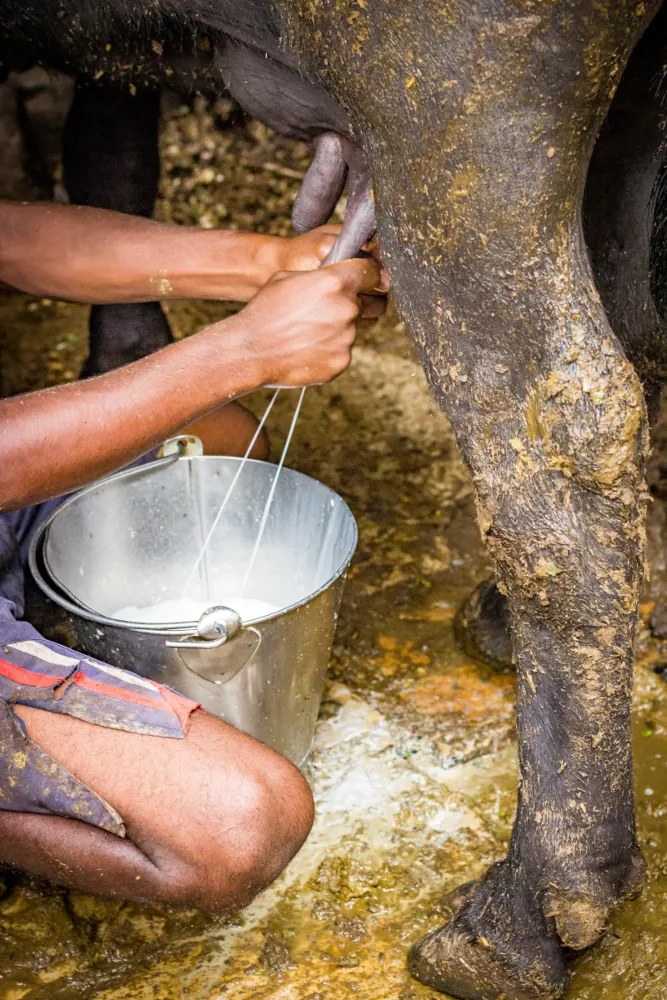

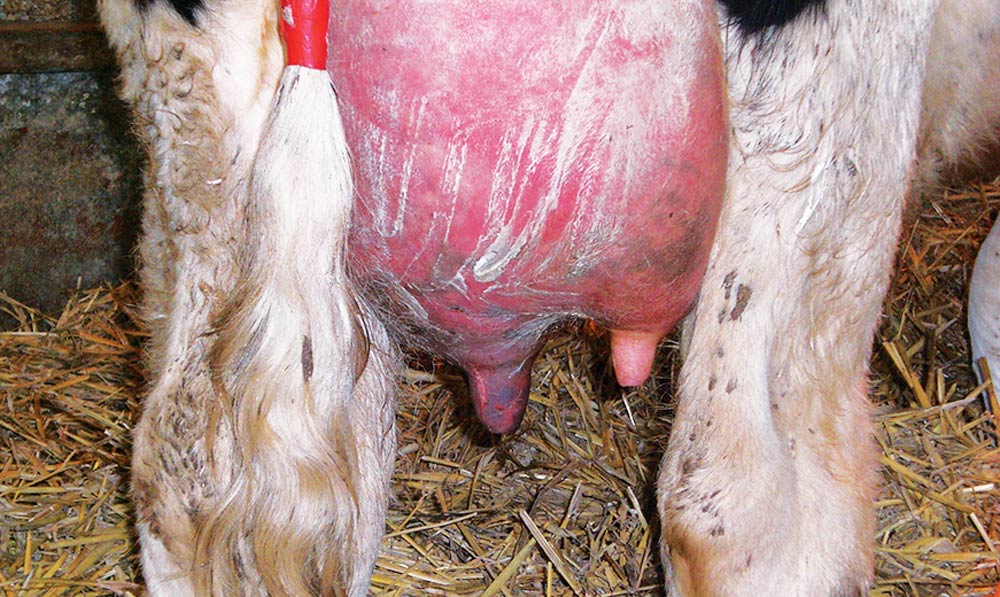
Mastitis occurs due to poor hygiene and over-milking. It is a painful inflammation of the mammary glands and is common among cows/buffaloes raised for their milk.
The pus from the infected udders often gets mixed with milk. Unlike in developed countries, in India, there is no regulation as to how many “pus cells per ml” should be allowed in milk. As a result, cows/buffaloes are milked even if they have mastitis. It is quite painful for the animal to be milked in such conditions. The animals are even tied to avoid resisting. To make things worse, modern milking machines keep on milking and do not stop until their sensors detect blood so that milk doesn’t appear pink.
Sperm Collection
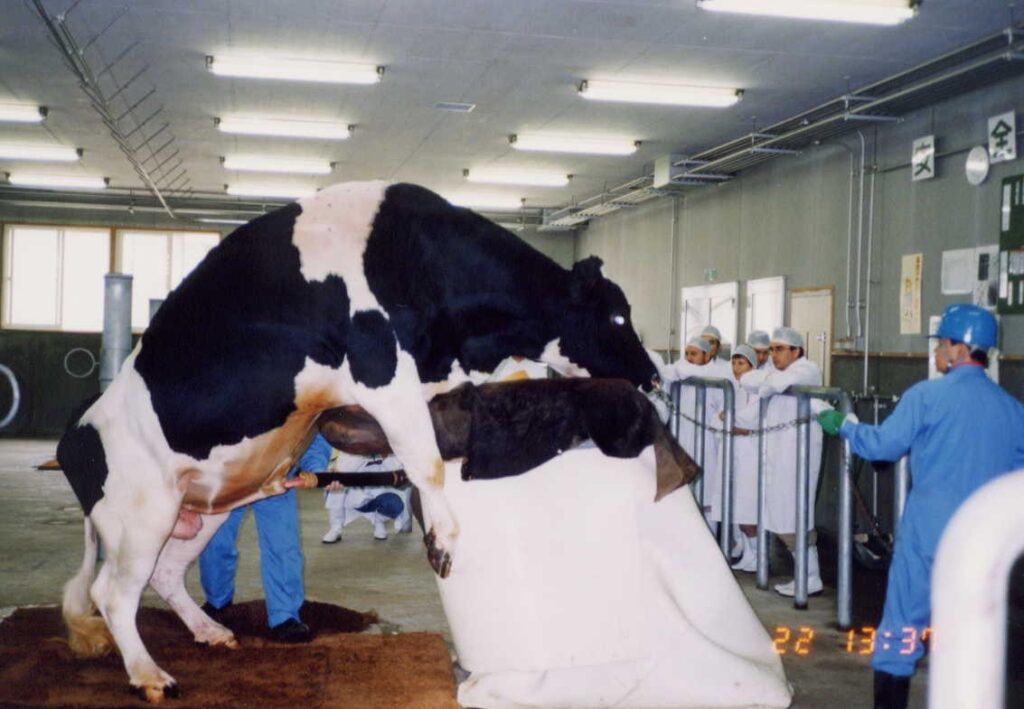

Sperm needed for artificial insemination is extracted from stud bulls either via the use of an artificial vagina or via electro-ejaculation with a rectal probe. This ‘probe’ is inserted in the anus of the restrained male animal where it sends in an electrical current, forcing the bull to ejaculate. Using an artificial vagina denies the pleasure of mating.
Read more: Artificially breeding cattle is cruel (to males): Madras HC
Abandonment
Some farmers choose not to slaughter their animals. However, it is not cheap to house all these animals once their milk production declines. Remember that farmers have to sell the milk at as low as ₹30/liter to dairies. It is only profitable to keep them for 5-6 years. But cows and buffaloes can live up to 15-20 years! As a result, many are abandoned. Animals that were fed by the farmers since birth suddenly find themselves on the streets. Moreover, our modern environments are not suitable for them. They starve and end up eating plastic bags which stay in their stomach forever.
Calves are also abandoned. States like Gujarat are filled with stray bulls that were abandoned at a young age.
You will also notice that there are far fewer stray buffaloes than cows even though most of the milk produced in India comes from buffaloes. This is because most buffaloes are slaughtered as soon as their milk production reduces.
Disbudding
Disbudding or dehorning makes sure that the calves do not grow horns.
It is performed on newborn calves!
Removing horns enables farmers to accommodate more animals in smaller space and reduces the risk of injury to other animals and humans. Dehorned animals have a higher market rate.
An iron rod heated over a flame or using electricity is pressed to burn the horn tissues of the calf! Painkillers and anesthesia are not always used. This causes immense pain and psychological trauma to the newborn calf.
Is cruelty-free milk possible?
Watch Arvind beautifully explain why milk from local farms and ahimsa milk too is full of cruelty:
62% of the total milk produced in India comes from small and medium farmers – source. Still, only 8.5% of buffaloes and 25% of cows are male – Livestock Census 2019. Also, India is the second largest exporter of beef in the world.
A rough calculation should make things clear: Imagine a farmer started his business 7 years ago with 10 cows. Assuming he/she impregnated each cow only 5 times, let’s calculate how many cows they should have today:
– If the Initial 10 cows were impregnated 5 times it would result in 50 new calves.
– These 50 new calves after 2 years of initial gap can be impregnated 5 times, resulting in 250 new calves!
– Hence the total calves after 7 years should be at least 10+50+250 = 360
You will find that the number of cows they should possess today is nowhere near what a small farmer would have in reality. Also, note that half of all new calves will be male and they are a burden on the business since they do not produce milk!
What to Do to Stop This Cruelty?
The easiest way is not to participate in such heinous acts. Milk is not made for us anyway. Ditch dairy, go vegan 🌱.
More Info on Cruelty in Dairy
Also read: Two-year undercover study reveals cruel side of India’s dairy industries
How fair is the milk industry?